Reflection Week 12 (Transformational Leadership)
The twelfth
class of Dynamics of Leadership was held on Tuesday, 11th June
2024. Today class starting with the Group 7 presentation title, ‘Transformational Leadership’. Just like
last week, Nurul Amirah has been appointed as SMT champion to conduct group
presentation session. Group 7 presenter are Mohamed Rohaizat, Nie Jing, Nur
Aliya, Nurul Amirah, Thoh and Xioana. All the group member has presented so
well and informative. From the presentation, what I understand that transformational
leadership is a leadership style that involves inspiring and motivating
followers to achieve exceptional performance and organizational outcomes. This
approach focuses on creating a positive and empowering work environment where
leaders encourage individual growth, foster innovation, and promote
organizational change. Transformational leaders are charismatic, visionary, and
capable of motivating and inspiring their team members to exceed expectations
and work towards a common vision.
After finish
group presentation, Prof Jamilah take over and continue the lecture on ‘Charismatic
and Transformational Leadership’. What is charismatic leadership? Max Weber (1900s) indicated charismatic leadership is
a type of leadership that involves being naturally personable, empathetic, and
inspiring to others who believe in you. Charismatic leadership describes a type
of leader who can motivate and influence others with their personality and
charm. A charismatic leader can motivate, inspire, and encourage others using
their strong communication skills and listening skills. Charismatic leaders
might appear to be natural leaders who are comfortable in their own skin and
can confidently manage a team with a clear vision.
The next slide
is about ‘Model of Personal Meaning and Charismatic Leadership’ that
consist leader personal meaning, leader behaviour and attributions of
charismatic leadership.
Prof Jamilah then discuss about the ‘Characteristics of charismatic leadership’. Below are the characteristics from the slide Prof Jamilah;
1. Self-confidence moral conviction - charismatic leaders exude self-confidence and have a strong sense of moral conviction. They believe in their vision and values, which instils confidence in their followers.
2. Inspires trust - charismatic leaders build trust by being authentic, transparent, and consistent in their words and actions. Their charisma and integrity help them earn the trust and loyalty of their team members.
3. High risk orientation - charismatic leaders are often willing to take risks and pursue bold ideas. Their courage and willingness to step outside the comfort zone can inspire others to do the same.
4. High energy Action orientation - charismatic leaders have high levels of energy and enthusiasm, which they channel into taking action and driving progress. Their passion for their vision energizes and motivates their followers.
5. Relational Power base - charismatic leaders build strong relationships with their followers based on trust, respect, and empathy. This relational power base allows them to influence and inspire others effectively.
6. Minimum internal conflict - charismatic leaders demonstrate emotional intelligence and are adept at managing internal conflicts and challenges. Their ability to remain composed and focused under pressure sets a positive example for their team.
7. Empowers others – charismatic leaders empower their team members by delegating responsibility, providing mentorship, and creating opportunities for growth and development. They encourage others to take ownership of their work and contribute to the team’s success.
8. Self-promoting - charismatic leaders effectively promote their vision, ideas, and initiatives in a confident and persuasive manner. They use their charisma and communication skills to garner support and enthusiasm for their goals.
9. Visionary - charismatic leaders have a clear and compelling vision for the future that inspires and motivates others. Their ability to communicate this vision in a way that resonates with their followers sets them apart as visionary leaders.
10. Verbal skills - charismatic leaders possess strong verbal communication skills, allowing them to articulate their vision, ideas, and goals effectively. They use persuasive language and storytelling to engage and inspire others
Next is about Four Strategies to develop Charismatic Qualities:
1. Develop visionary skills – communicate a vision with passion, aligns goals with aspirations, and lead by example with dedication and enthusiasm.
2. Practice being candid – embrace your uniqueness & values, as genuine charisma comes from being sincere and real
3. Improve Communication – enhance verbal and nonverbal skills and active listening to convey confidence and sincerity
4. Cultivate Emotional Intelligence – develop empathy, self-awareness and social skills to connect with others deeply and inspire trust and loyalty.
There are 2
types of charismatic leadership, which is personalized
charismatic leader and socialized charismatic leader. Refer
below table for the differences;
|
|
Personalized
Charismatic Leadership |
Socialized
Charismatic Leadership |
|
Focus |
Focuses on the leader's own charisma, personality, and individual
qualities as the source of influence and inspiration for their followers. |
Emphasizes building a collective identity and shared vision
within the group or organization. The leader focuses on empowering and
involving others in decision-making and goal-setting. |
|
Approach to Power |
Personalized charismatic leaders often rely on their personal
charm and influence to motivate and inspire followers. They may centralize
power and decision-making in their own hands, leading to a cult of
personality around them. |
Socialized charismatic leaders seek to distribute power and
decision-making among team members. They cultivate a sense of shared
responsibility and ownership of the vision and goals, encouraging
collaboration and teamwork. |
|
Long-Term Sustainability |
Personalized charismatic leadership can be effective in the short
term, as the leader's charisma can quickly inspire followers. However, it may
not be sustainable in the long run, as it depends heavily on the leader's
individual qualities and may not foster the development of leadership
capabilities in others. |
Socialized charismatic leadership is often more sustainable in
the long term, as it focuses on building a strong organizational culture and
collective identity that can outlast any individual leader. This approach
encourages the development of leadership qualities in multiple team members,
creating a more resilient and adaptable organization. |
|
Communication |
May use charismatic and persuasive communication to rally support
and inspire followers. |
Emphasize transparent and inclusive communication that fosters
collaboration and engagement among team members. |
|
Example of leader |
Adolf Hitler, David Koresh |
Nelson Mandela, Martin Luther King, Jr. |
Ok next we
moved to discussed about ‘Transactional Leadership’.
The
transactional style of leadership, originally introduced by Max Weber in 1947
and further elaborated by Bernard Bass in 1981, is commonly adopted by
management. Transactional leadership is a style of leadership that focuses on
the exchange or transaction between the leader and their followers. In a
transactional leadership model, the leader motivates and directs their
followers by setting clear expectations, providing rewards for meeting
performance goals, and using punishments for failure to meet expectations. This
style of leadership is based on the idea of a "transaction" or
exchange of effort for reward or punishment. Employees are given short- and
long-term goals, work under supervision, and adhere to strict company
guidelines. Those who meet their goals are rewarded, while those who miss
deadlines face reprimands. Unlike transformational leadership, which
encourages creativity and thinking outside the box, transactional leadership
thrives in environments that prioritize organization and structure.
I listed below the Key characteristics of transactional leadership include:
1. Contingent Rewards: Transactional leaders clarify the expectations and goals for their followers and establish a system of rewards for meeting or exceeding these expectations. This may involve incentives such as bonuses, promotions, or recognition for good performance.
2. Management by Exception: Transactional leaders also monitor performance closely and intervene to correct deviations from expectations. They may use management by exception, which involves addressing issues only when they fall below a certain standard or when problems arise.
3. Passive Management by Exception: Some transactional leaders practice a form of passive management by exception, in which they intervene only when problems occur or when performance deviates significantly from expectations.
4. Active Management by Exception: Other transactional leaders practice active management by exception, which involves more proactive monitoring of performance and intervening to address issues before they escalate.
5. Laissez-Faire: In some cases, transactional leaders may also demonstrate a laissez-faire approach, allowing followers to work independently with minimal guidance or direction.
Transactional
leadership can be effective in situations where followers are motivated by
rewards, clear guidelines, and accountability. However, this leadership style
may limit creativity, innovation, and intrinsic motivation among followers, as
it relies heavily on external rewards and punishments to drive performance.
Transactional
leadership is often contrasted with transformational leadership, which focuses
on inspiring and motivating followers to achieve higher levels of performance
through shared vision, empowerment, and personal growth. Both transactional
and transformational leadership styles have their own strengths and
weaknesses, and some leaders may use a combination of both approaches
depending on the situation and the needs of their followers.
Below are strengths and weaknesses of ‘Transactional Leadership’:
|
Transactional
Leadership |
|
|
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|
Clear Expectations:
Transactional leaders provide clear expectations and guidelines for their
followers, which can help improve performance and accountability. |
Lack of Innovation: The emphasis
on rewards and punishments may stifle creativity and innovation among
followers, as they may focus more on meeting expectations than exploring new
ideas. |
|
Goal-Oriented: This
leadership style focuses on achieving specific goals and targets, which can
be beneficial in situations where tasks need to be completed efficiently and
effectively. |
Limited Engagement:
Transactional leadership may not inspire high levels of engagement or
commitment from followers, as it primarily relies on external motivations
rather than intrinsic motivation. |
|
Rewards and Punishments:
Transactional leaders use rewards and punishments to motivate and guide their
followers, which can help drive performance and maintain discipline. |
Transactional Exchange: The focus
on a transactional exchange between the leader and followers can create a
sense of "doing the minimum required" rather than going above and
beyond expectations. |
|
Immediate Feedback:
Transactional leadership typically involves monitoring performance closely
and providing immediate feedback on progress, allowing for timely corrections
and adjustments. |
Short-Term Focus:
Transactional leadership is often more focused on short-term goals and
results, which may hinder long-term strategic thinking and planning. |
We go for ‘Transformational
Leadership’. Transformational leadership style, as described by Bernard
M. Bass in 1985, focuses on inspiring and motivating followers to achieve
their best, ultimately transforming their outlook and behaviour. This style
involves empowering and developing followers to reach their full potential,
fostering creative and innovative thinking, and promoting a strong sense of
shared vision and values.
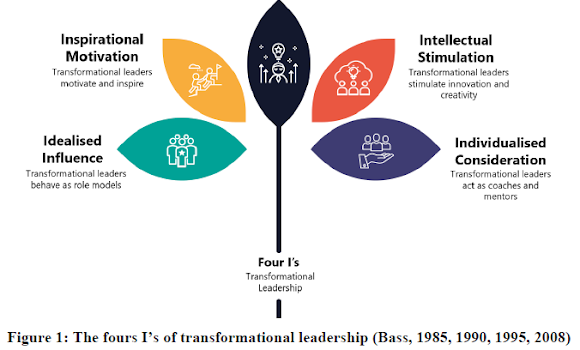
According to (Ahmed Waham, Abdul Rahman, & Wan Mustaffa, 2020), transformational leadership is based on four I’s characteristics, as shown as figure 1 below;
Transformational leadership is often characterized by the following key dimensions (as figure shown above):
1. Idealized Influence (Charisma): This dimension reflects the leader's ability to establish trust, respect, and admiration among followers by serving as a role model and embodying desirable qualities such as integrity, authenticity, and moral courage. Transformational leaders inspire followers to emulate their behaviour and values.
2. Inspirational Motivation: Transformational leaders articulate a compelling vision for the future, set high expectations, and inspire followers to work towards shared goals. They use effective communication, storytelling, and passion to energize and mobilize individuals to commit to the vision and mission of the organization.
3. Intellectual Stimulation: Transformational leaders encourage creativity, critical thinking, and innovation among followers by challenging assumptions, fostering a culture of learning and open dialogue, and promoting intellectual curiosity. They empower individuals to question the status quo, explore new ideas, and develop their problem-solving skills.
4. Individualized Consideration: Transformational leaders demonstrate care, empathy, and support for the needs and development of each individual follower. They create a personalized and inclusive environment where individuals feel valued, respected, and empowered to contribute their unique strengths and perspectives. Transformational leaders provide coaching, mentoring, and feedback to help individuals grow and thrive.
Now, we go for
the strengths and weaknesses of ‘Transformational Leadership’:
Below are strengths
and weaknesses of ‘Transformational Leadership’:
|
Transformational
Leadership |
|
|
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|
Inspirational Vision:
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate followers by articulating a
compelling vision and shared goals, creating a sense of purpose and meaning. |
Idealism: The emphasis
on vision, inspiration, and empowerment may sometimes be seen as overly
idealistic and lacking concrete direction or guidelines. |
|
Empowerment: This
leadership style empowers followers to take ownership of their work, make
decisions, and contribute to the overall success of the organization. |
Resistance to Change: Some
followers may resist change or feel overwhelmed by the high expectations set
by transformational leaders, leading to potential challenges in
implementation. |
|
Development of Followers:
Transformational leaders focus on developing the skills, capabilities, and
potential of their followers, fostering personal and professional growth. |
Dependency: Followers
may become overly reliant on the leader for motivation and guidance,
potentially hindering their ability to take initiative and act independently. |
|
Creativity and Innovation:
Transformational leadership encourages creativity, innovation, and
risk-taking among followers, leading to new ideas and solutions. |
Potential for Burnout:
Transformational leaders may invest a significant amount of time and energy
into inspiring and developing their followers, which could lead to burnout if
not managed effectively. |
From the above
discussion about transactional and transformation leadership, I may conclude
that transformational leadership models emphasize the importance of
building strong relationships, nurturing a positive organizational culture, and
empowering followers to reach their full potential. By focusing on both the
individual and collective growth of their followers, transformational leaders
can inspire higher levels of performance, engagement, and commitment within
their teams or organizations.
It's worth
noting that transformational leadership is often contrasted with transactional
leadership, which focuses more on managing the exchange of rewards and
punishments to motivate followers. While transactional leaders emphasize
performance goals, accountability, and compliance, transformational leaders aim
to inspire, empower, and develop individuals to create lasting positive change
and achieve shared goals.
From Youtube video: https://youtu.be/ddt_IGMMOrI
Below are the examples of Transformational leader in the world;
1. Mahatma Gandhi: Gandhi is widely regarded as one of the most transformative leaders in history due to his nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience movements that played a crucial role in India's struggle for independence from British colonial rule. Gandhi's principled stance on nonviolence, moral leadership, and commitment to social justice inspired millions of people and led to significant political and social change.
2. Nelson Mandela: The former President of South Africa, is hailed as a transformational leader for his role in dismantling apartheid and promoting reconciliation and unity in a divided nation. Mandela's vision of a democratic, inclusive society, his ability to forgive and forget relationships across racial lines, and his unwavering commitment to justice and equality made him a symbol of resilience and hope for people around the world.
3. Martin Luther King Jr.: A transformative leader in the American civil rights movement, advocating for nonviolent activism, racial equality, and social justice. King's powerful speeches, moral courage, and commitment to peaceful protest were instrumental in challenging systemic racism and inspiring positive change through the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
4. Steve Jobs: The co-founder and former CEO of Apple Inc., is widely regarded as a transformational leader in the technology industry. Known for his innovation, creative vision, and commitment to excellence, Jobs revolutionized the way we use and interact with technology through products like the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook. His leadership style, focus on design, and relentless pursuit of perfection have had a lasting impact on the tech industry and beyond.
5. Mark Zuckerberg: The co-founder and CEO of Facebook, has had a significant impact on social media and digital communication as a transformational leader in the tech industry. Through Facebook, Zuckerberg has connected billions of people around the world, transformed the way we share information and interact online, and sparked conversations about privacy, data security, and the role of technology in society.
6. Elon Musk: The CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, is a transformative leader in the fields of electric vehicles, renewable energy, and space exploration. Musk's ambitious vision, technological innovation, and commitment to sustainability have reshaped industries and pushed boundaries in the pursuit of innovation, with goals ranging from reducing carbon emissions to colonizing Mars.
Last but not
least, a lecture from Prof Jamilah today is about the Servant Leadership
style. The concept of servant leadership originated from Robert
Greenleaf, who was the first to develop and conceptualize this leadership
style. Robert Greenleaf emphasized the importance of serving others first in
leadership, rather than focusing solely on leading (Rachmawati & Lantu, 2014).
Below are the Key principles of the Servant Leadership style as outlined by Robert K. Greenleaf include:
1. Service to Others: The core tenet of servant leadership is the idea that leaders should focus on serving the needs of others, whether they are employees, colleagues, or the broader community. By prioritizing the well-being and growth of their followers, servant leaders aim to empower, support, and uplift others to reach their full potential.
2. Empathy and Listening: Servant leaders practice active listening, empathy, and compassion towards others. They seek to understand the perspectives, needs, and concerns of their team members, and they create a supportive and inclusive environment where individuals feel valued, heard, and respected.
3. Healing and Growth: Servant leaders are committed to promoting the personal and professional growth of their followers. They provide guidance, mentorship, and opportunities for development, and they create a culture that encourages learning, innovation, and continuous improvement.
4. Community Building: Servant leadership emphasizes the importance of building strong, cohesive communities within organizations. Servant leaders foster a sense of belonging, collaboration, and shared purpose among team members, promoting trust, teamwork, and a spirit of unity.
5. Awareness and Persuasion: Servant leaders are self-aware and introspective, recognizing their own strengths, weaknesses, and biases. They lead by example, using persuasion, influence, and ethical behaviour to inspire and motivate others rather than relying on authority or coercion.
6. Conceptualization and Foresight: Servant leaders have a long-term vision and strategic perspective. They are able to think creatively, anticipate future challenges and opportunities, and guide their organizations towards sustainable success through thoughtful planning and decision-making.
One notable example of a servant leader in the world is Mahatma Gandhi. Gandhi, a prominent figure in India's struggle for independence from British colonial rule, exemplified the principles of servant leadership through his selfless dedication to serving others, promoting nonviolent resistance, and inspiring social change through his actions and beliefs. Mahatma Gandhi's servant leadership style and his legacy of nonviolent resistance, social justice, and human rights continue to inspire leaders and activists around the world. By embodying the principles of service, empathy, empowerment, and community-building, Gandhi demonstrated the transformative impact that servant leadership can have on individuals, societies, and movements for positive change.
|
Key
characteristics of Mahatma Gandhi's servant leadership |
|
|
|
|
|
Commitment to Service: |
Gandhi dedicated his life to serving the people of India and
advancing the cause of freedom and social justice. He lived a simple and humble
life, putting the needs of others above his own personal interests and
demonstrating a deep commitment to the well-being of his followers. |
|
Empathy and Compassion: |
Gandhi was known for his compassion towards all individuals,
regardless of their background or beliefs. He emphasized the importance of
understanding and respecting the perspectives and experiences of others,
promoting unity and harmony among diverse communities. |
|
Nonviolent Resistance: |
Gandhi advocated for nonviolent resistance as a means of
achieving social and political change. He believed in the power of peaceful
protests, civil disobedience, and moral persuasion to overcome injustice and
oppression, inspiring others to follow his example. |
|
Inspiring and Empowering Others: |
Gandhi empowered individuals to take action and be agents of
change in their communities. He led by example, demonstrating courage,
integrity, and moral strength, and he encouraged others to stand up for their
beliefs and work towards a more just and equitable society. |
|
Building Community: |
Gandhi emphasized the importance of building strong, inclusive
communities based on mutual respect, cooperation, and dialogue. He sought to
bridge divisions, promote understanding, and create a sense of unity among
people from different backgrounds and walks of life. |
|
Vision and Selflessness: |
Gandhi had a clear vision for India's independence and the social
reforms he sought to achieve. He was willing to make personal sacrifices,
endure hardship, and face adversity in pursuit of his ideals, placing the
interests of the larger community above his own self-interest. |
In summary, the
Servant Leadership style introduced by Robert K. Greenleaf has had a lasting
impact on leadership theory and practice, inspiring leaders to adopt a more
people-centred, ethical, and values-driven approach to leadership. By
emphasizing service, empathy, collaboration, and community-building, servant
leaders aim to create positive organizational cultures, empower their
followers, and contribute to the well-being and success of individuals and
communities.
Last but not
least, to end up this week reflection, I want to share another example of
Servant Leadership by the late Allahyarham Nik Aziz Nik Mat, a former
Spiritual Leader (Murshid’il Am) of the Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (PAS) that
may be considered as a Servant Leader. Actually, I admire the late Allahyarham
for his humble and modest lifestyle, unlike other politicians in Malaysia. His
dedication to serving the people and commitment to honesty set him apart from
the rest. He truly embodied the values of integrity and selflessness, and his
legacy will continue to inspire others for generations to come. May his soul
rest in peace.
Below are the
characteristics that can be considered as Servant leadership style:
|
Key
characteristics of Allahyarham Nik Aziz Nik Mat’s Servant leadership style |
|
|
|
|
|
Commitment to Service: |
Nik Aziz dedicated his life to serving the people of Kelantan,
prioritizing their needs and interests above his own. He was known for his
simplicity, humility, and unwavering dedication to upholding the principles
of justice, integrity, and social welfare. |
|
Empathy and Compassion: |
Nik Aziz demonstrated empathy and compassion towards the people
he served, showing genuine care for their well-being and addressing their
concerns with understanding and sensitivity. He prioritized the needs of the
less fortunate and marginalized members of society, advocating for social
justice and equality. |
|
Leading by Example: |
Nik Aziz led by example, living a modest and disciplined life
that reflected his values and principles. He eschewed personal luxuries and
focused on serving others, setting a positive example for his followers and
inspiring them to uphold similar values of humility, honesty, and integrity. |
|
Promoting Social Justice: |
Nik Aziz was a strong advocate for social justice, equality, and
human rights, working to improve the lives of the people of Kelantan through
policies and initiatives that aimed to uplift the disadvantaged and
marginalized communities. He championed causes such as poverty alleviation,
education, healthcare, and environmental conservation. |
|
Community Building: |
Nik Aziz emphasized the importance of building strong and
cohesive communities based on mutual respect, solidarity, and cooperation. He
promoted unity among the diverse ethnic and religious groups in Kelantan,
fostering a sense of inclusivity and belonging among the residents of the
state. |
|
Spiritual Leadership: |
Nik Aziz's leadership was guided by his deep spiritual beliefs
and principles rooted in Islamic teachings. He sought to lead with wisdom,
compassion, and moral integrity, drawing inspiration from his faith to guide
his actions and decisions as a leader. |
As usual for
all the session ended by Prof Jamilah a momento word ‘In the world you can be anything,
be kind, in life always remember, what you give, you get back’.




Comments
Post a Comment